Create a Feedback Dataset#
The Feedback Task datasets allow you to combine multiple questions of different kinds, so the first step will be to define the aim of your project and the kind of data and feedback you will need to get there. With this information, you can start configuring a dataset and formatting records using the Python SDK.
This guide will walk you through all the elements you will need to configure to create a FeedbackDataset and add records to it.
Note
To follow the steps in this guide, you will first need to connect to Argilla. Check how to do so in our cheatsheet.
Define record fields#
A record in Argilla refers to a data item that requires annotation and can consist of one or multiple fields i.e., the pieces of information that will be shown to the user in the UI in order to complete the annotation task. This can be, for example, a prompt and output pair in the case of instruction datasets.
As part of the FeedbackDataset configuration, you will need to specify the list of fields to show in the record card. As of Argilla 1.8.0, we only support one type of field, TextField, which is a plain text field. We have plans to expand the range of supported field types in future releases of Argilla.
You can define the fields using the Python SDK providing the following arguments:
name: The name of the field, as it will be seen internally.title(optional): The name of the field, as it will be displayed in the UI. Defaults to thenamevalue, but capitalized.required(optional): Whether the field is required or not. Defaults toTrue. Note that at least one field must be required.use_markdown(optional): Sepcify whether you want markdown rendered in the UI. Defaults toFalse.
fields = [
rg.TextField(name="question", required=True),
rg.TextField(name="answer", required=True, use_markdown=True),
]
Note
The order of the fields in the UI follows the order in which these are added to the fields attribute in the Python SDK.
Define questions#
To collect feedback for your dataset, you need to formulate questions. The Feedback Task currently supports the following types of questions:
RatingQuestion: These questions require annotators to select one option from a list of integer values. This type is useful for collecting numerical scores.TextQuestion: These questions offer annotators a free-text area where they can enter any text. This type is useful for collecting natural language data, such as corrections or explanations.LabelQuestion: These questions ask annotators to choose one label from a list of options. This type is useful for text classification tasks. In the UI, the labels of theLabelQuestionwill have a rounded shape.MultiLabelQuestion: These questions ask annotators to choose all applicable labels from a list of options. This type is useful for multi-label text classification tasks. In the UI, the labels of theMultiLabelQuestionwill have a squared shape.
You can define your questions using the Python SDK and set up the following configurations:
name: The name of the question, as it will be seen internally.title(optional): The name of the question, as it will be displayed in the UI. Defaults to thenamevalue, but capitalized.required(optional): Whether the question is required or not. Defaults toTrue. Note that at least one question must be required.description(optional): The text to be displayed in the question tooltip in the UI. You can use it to give more context or information to annotators.
The following arguments apply to specific question types:
values: The rating options to answer theRatingQuestion. It can be any list of unique integers. It doesn’t matter whether these are positive, negative, sequential or not.labels: InLabelQuestionandMultiLabelQuestionthis is a list of strings with the options for these questions. If you’d like the text of the labels to be different in the UI and internally, you can pass a dictionary instead where the key is the internal name and the value the text to display in the UI.visible_labels(optional): InLabelQuestionandMultiLabelQuestionthis is the number of labels that will be visible in the UI. By default, the UI will show 20 labels and collapse the rest. Set your preferred number to change this limit or setvisible_labels=Noneto show all options.use_markdown(optional): InTextQuestiondefine whether the field should render markdown text. Defaults toFalse.
Check out the following tabs to learn how to set up questions according to their type:
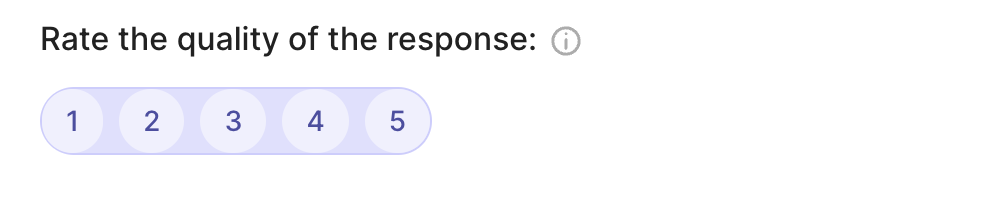
rg.RatingQuestion(
name="rating",
title="Rate the quality of the response:",
description="1 = very bad - 5= very good",
required=True,
values=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
)
rg.TextQuestion(
name="corrected-text",
title="Provide a correction to the response:",
required=False,
use_markdown=True
)

rg.LabelQuestion(
name="relevant",
title="Is the response relevant for the given prompt?",
labels=["Yes","No"],
required=True,
visible_labels=None
)

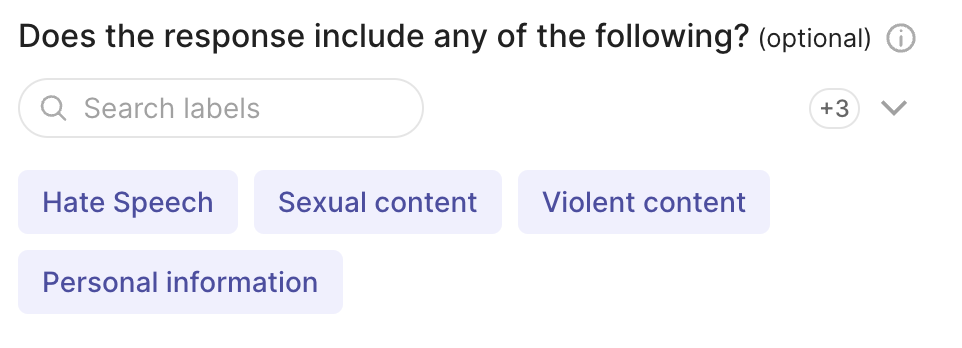
rg.MultiLabelQuestion(
name="content_class",
title="Does the response include any of the following?",
description="Select all that apply",
labels={"hate": "Hate Speech" , "sexual": "Sexual content", "violent": "Violent content", "pii": "Personal information", "untruthful": "Untruthful info", "not_english": "Not English", "inappropriate": "Inappropriate content"},
required=False,
visible_labels=4
)
Define guidelines#
Once you have decided on the data to show and the questions to ask, it’s important to provide clear guidelines to the annotators. These guidelines help them understand the task and answer the questions consistently. You can provide guidelines in two ways:
In the dataset guidelines: this is added as an argument when you create your dataset in the Python SDK (see below). It will appear in the dataset settings in the UI.
As question descriptions: these are added as an argument when you create questions in the Python SDK (see above). This text will appear in a tooltip next to the question in the UI.
It is good practice to use at least the dataset guidelines if not both methods. Question descriptions should be short and provide context to a specific question. They can be a summary of the guidelines to that question, but often times that is not sufficient to align the whole annotation team. In the guidelines, you can include a description of the project, details on how to answer each question with examples, instructions on when to discard a record, etc.
Configure the dataset#
Once the scope of the project is defined, which implies knowing the fields, questions and guidelines (if applicable), you can proceed to create the FeedbackDataset. To do so, you will need to define the following arguments:
fields: The list of fields to show in the record card. The order in which the fields will appear in the UI matches the order of this list.questions: The list of questions to show in the form. The order in which the questions will appear in the UI matches the order of this list.guidelines(optional): A set of guidelines for the annotators. These will appear in the dataset settings in the UI.
If you haven’t done so already, check the sections above to learn about each of them.
Below you can find a quick example where we create locally a FeedbackDataset to assess the quality of a response in a question-answering task. The FeedbackDataset contains two fields, question and answer, and two questions to measure the quality of the answer and to correct it if needed.
dataset = rg.FeedbackDataset(
guidelines="Please, read the question carefully and try to answer it as accurately as possible.",
fields=[
rg.TextField(name="question"),
rg.TextField(name="answer"),
],
questions=[
rg.RatingQuestion(
name="answer_quality",
description="How would you rate the quality of the answer?",
values=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
),
rg.TextQuestion(
name="answer_correction",
description="If you think the answer is not accurate, please, correct it.",
required=False,
),
]
)
Note
Fields and questions in the UI follow the order in which these are added to the fields and questions atrributes in the Python SDK.
Hint
If you are working as part of an annotation team and you would like to control how much overlap you’d like to have between your annotators, you should consider the different workflows in the Set up your annotation team guide before configuring and pushing your dataset.
Add records#
At this point, we just need to add records to our FeedbackDataset. Take some time to explore and find data that fits the purpose of your project. If you are planning to use public data, the Datasets page of the Hugging Face Hub is a good place to start.
Tip
If you are using a public dataset, remember to always check the license to make sure you can legally employ it for your specfic use case.
from datasets import load_dataset
# load and inspect a dataset from the Hugging Face Hub
hf_dataset = load_dataset('databricks/databricks-dolly-15k', split='train')
df = hf_dataset.to_pandas()
df
Hint
Take some time to inspect the data before adding it to the dataset in case this triggers changes in the questions or fields.
The next step is to create records following Argilla’s FeedbackRecord format. These are the attributes of a FeedbackRecord:
fields: A dictionary with the name (key) and content (value) of each of the fields in the record. These will need to match the fields set up in the dataset configuration (see Define record fields).external_id(optional): An ID of the record defined by the user. If there is no external ID, this will beNone.responses(optional): A list of all responses to a record. There is no need to configure this when creating a record, it will be filled automatically with the responses collected from the Argilla UI.
# create a single Feedback Record
record = rg.FeedbackRecord(
fields={
"question": "Why can camels survive long without water?",
"answer": "Camels use the fat in their humps to keep them filled with energy and hydration for long periods of time."
},
external_id=None
)
As an example, here is how you can transform a whole dataset into records at once, renaming the fields and optionally filtering the original dataset:
records = [rg.FeedbackRecord(fields={"question": record["instruction"], "answer": record["response"]}) for record in hf_dataset if record["category"]=="open_qa"]
Now, we simply add our records to the dataset we configured above:
#add records to the dataset
dataset.add_records(records)
Push to Argilla#
To import the dataset to your Argilla instance with the FeedbackDataset.push_to_argilla() method. Once pushed, you will be able to see your dataset in the UI.
dataset.push_to_argilla(name="my-dataset", workspace="my-workspace")
Now you’re ready to start the annotation process.

