🤗 Build a custom sentiment classifier with SetFit and Argilla#
In this tutorial, we’ll build a sentiment classifier for user requests in the banking domain using SetFit and Argilla.
SetFit is an exciting open-source package for few-shot classification developed by teams at Hugging Face and Intel Labs. You can read all about it on the project repository.
Argilla empowers you to quickly build and iterate on training data for NLP.
Let’s see how to combine them to build a sentiment classifier from scratch!
Introduction#
This tutorial will show you how to fine-tune a sentiment classifier for your own domain, starting with no labeled data.
Most online tutorials about fine-tuning models assume you already have a training dataset. You’ll find many tutorials for fine-tuning a pre-trained model with widely-used datasets, such as IMDB for sentiment analysis.
However, often what you want is to fine-tune a model for your use case. It’s well-known that NLP model performance usually degrades with “out-of-domain” data. For example, a sentiment classifier pre-trained on movie reviews (e.g., IMDB) will not perform very well with customer requests.
Setup#
In this tutorial, we’ll use setfit and datasets libraries.
[ ]:
%pip install setfit datasets -qqq
Let’s import the modules we need:
[2]:
from datasets import load_dataset
import argilla as rg
from sentence_transformers.losses import CosineSimilarityLoss
from setfit import SetFitModel, SetFitTrainer
Source dataset: banking77#
The banking77, available on the Hugging Face Hub, contains online banking user queries annotated with their corresponding intents.
In our case, we’ll label the sentiment of these queries. This might be useful for digital assistants and customer service analytics.
Let’s load the dataset directly from the Hub.
[ ]:
banking_ds = load_dataset("banking77", split="train")
Let’s get a preview of the dataset’s content using Pandas head method:
[5]:
banking_ds.to_pandas().head(15)
[5]:
| text | label | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | I am still waiting on my card? | 11 |
| 1 | What can I do if my card still hasn't arrived ... | 11 |
| 2 | I have been waiting over a week. Is the card s... | 11 |
| 3 | Can I track my card while it is in the process... | 11 |
| 4 | How do I know if I will get my card, or if it ... | 11 |
| 5 | When did you send me my new card? | 11 |
| 6 | Do you have info about the card on delivery? | 11 |
| 7 | What do I do if I still have not received my n... | 11 |
| 8 | Does the package with my card have tracking? | 11 |
| 9 | I ordered my card but it still isn't here | 11 |
| 10 | Why has my new card still not come? | 11 |
| 11 | I still haven't received my card after two wee... | 11 |
| 12 | Can you track my card for me? | 11 |
| 13 | Is there a way to track the delivery of my card? | 11 |
| 14 | It's been a week since I ordered my card and i... | 11 |
A note on sentiment analysis and data annotation#
Sentiment analysis is one of the most subjective tasks in NLP. What we understand by sentiment will vary from one application to another and depend on the business objectives of the project. Also, sentiment can be modeled in different ways, leading to different labeling schemes.
For example, sentiment can be modeled as real value (going from -1 to 1, from 0 to 1.0, etc.) or with 2 or more labels (including different degrees such as positive, negative, neutral, etc.)
For this tutorial, we’ll use the following labeling scheme: POSITIVE, NEGATIVE and NEUTRAL.
1. Load the dataset and label a few examples#
[ ]:
argilla_ds = rg.read_datasets(banking_ds, task="TextClassification")
rg.log(argilla_ds, "banking_sentiment")
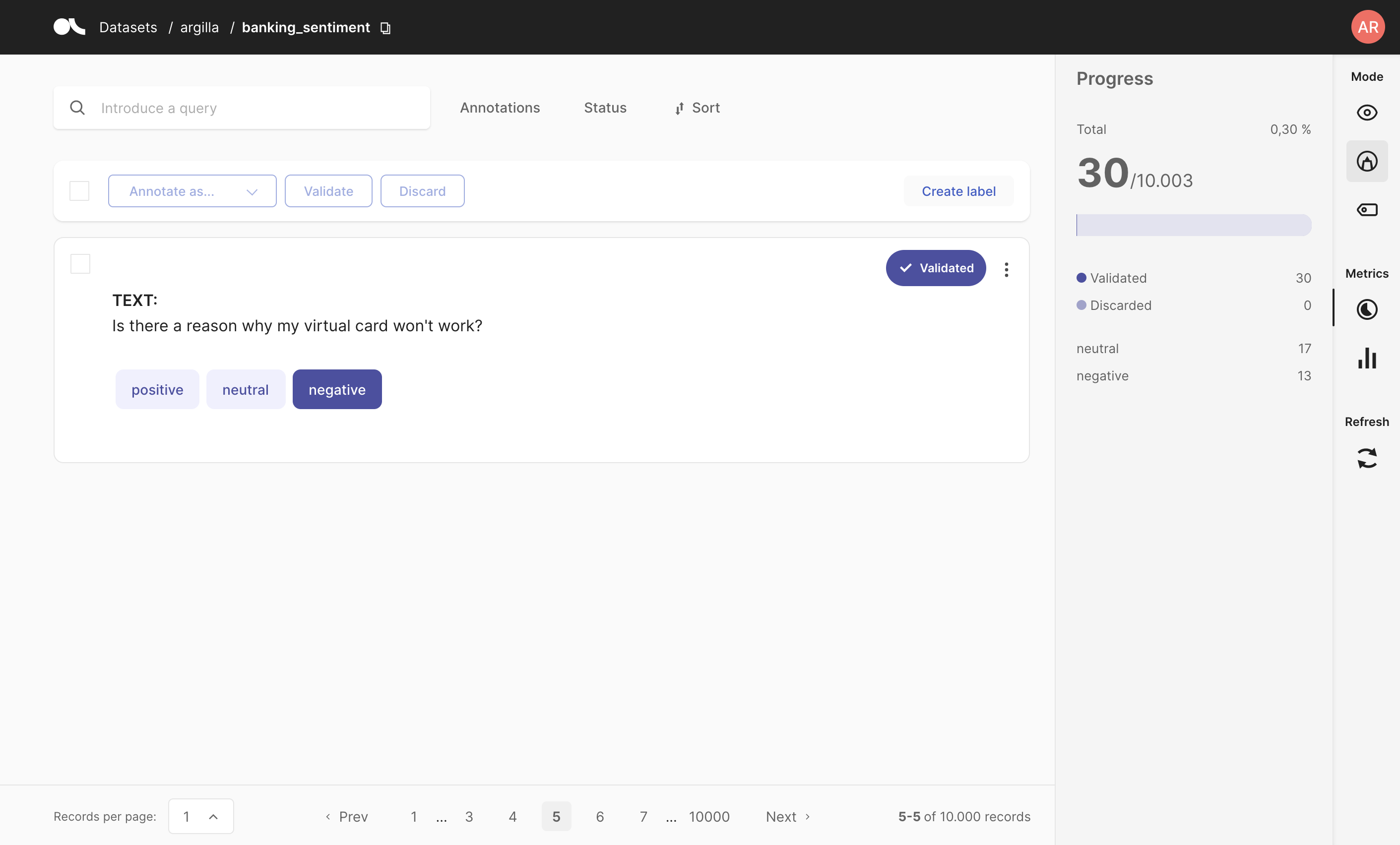
2. Hand labelling#
In this step, you can use Argilla UI to label a few examples (e.g., 50 examples).
Once you have labelled a few example, you can read and prepare the data for training your SetFit model.
Note
If you don’t have time for labeling now we have labelled a small dataset with Argilla and pushed it to the Hugging Face Hub.
To use it replace the below cell with this code:
`labelled_ds = load_dataset("argilla/sentiment-banking-setfit")`
[8]:
labelled_ds = rg.load("banking_sentiment").prepare_for_training()
labelled_ds = labelled_ds.train_test_split()
labelled_ds
[8]:
DatasetDict({
train: Dataset({
features: ['text', 'label'],
num_rows: 108
})
test: Dataset({
features: ['text', 'label'],
num_rows: 36
})
})
3. Train our SetFit sentiment classifier#
[9]:
model = SetFitModel.from_pretrained("sentence-transformers/paraphrase-mpnet-base-v2")
# Create trainer
trainer = SetFitTrainer(
model=model,
train_dataset=labelled_ds["train"],
eval_dataset=labelled_ds["test"],
loss_class=CosineSimilarityLoss,
batch_size=8,
num_iterations=20,
)
trainer.train()
metrics = trainer.evaluate()
metrics
model_head.pkl not found on HuggingFace Hub, initialising classification head with random weights.
108 train samples in total, 540 train steps with batch size 8
[9]:
{'accuracy': 0.8611111111111112}
Here we are using the simplest approach for training our SetFit model. Since it integrates with Optuna, you could use hyperparameter tuning to find the best hyperparamaters for training your model. However, it is better to start with a simple baseline, validate the model for your use case and iterate on the data before focusing on model experimentation and tuning.
Summary#
In this tutorial, you learned how to build a training set from scratch and train a sentiment classifier for your own problem.
Although this is a simple example, you can apply this same process to your own use case.
Here, we’ve covered one way of building training sets: hand labeling.
If you are interested in SetFit, you can check this other tutorial.
If want to discover other methods like weak supervision or active learning check the following tutorials:
Next steps#
🙋♀️ Join the Argilla Slack community
📚 Argilla documentation for more guides and tutorials.

